
Shree Ramkrishna Netralaya... The Eye care center collaborated with Carl Zeiss the 1st Myopia Clinic in Mumbai/ West India/ Maharashtra on July 8, 2023 for the noble initiative.



Myopia or near-sightedness is a condition in which close objects appear clear but distant objects appear blurry. It is one of the major public health concerns around the world, with a prediction that nearly 50% of the global population will be myopic by 2050.
Myopia is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Other factors include prolonged near work, insufficient time outdoors, and family history. Post-COVID-19 period kids have seen more time being spent on digital screens, phones, laptops, and tablets for their school homework. This excessive screen time for a long duration can cause Myopia.
Different types of treatments are available but in today's time, the best and the easiest methods available are Pharmacological Therapy and special spectacle glasses. These glasses are available in India for the last one year, and when used by children the number stops increasing. In fact, studies suggest that using glasses can stop the progression of Myopia by 55%-60%. This is how we can control Myopia and tame it.
ZEISS has this comprehensive Myopia Spectacles glasses which will control the Myopia Progression 55%-60%. This special glass will be dispensed in the Myopia Clinic concept as one of the treatments. To early detection and treatment for children,
ZEISS has also taken the initiative to support the Shree Ramkrishna Netralaya eye care center to launch Myopia Clinic to control Myopia progression in India.
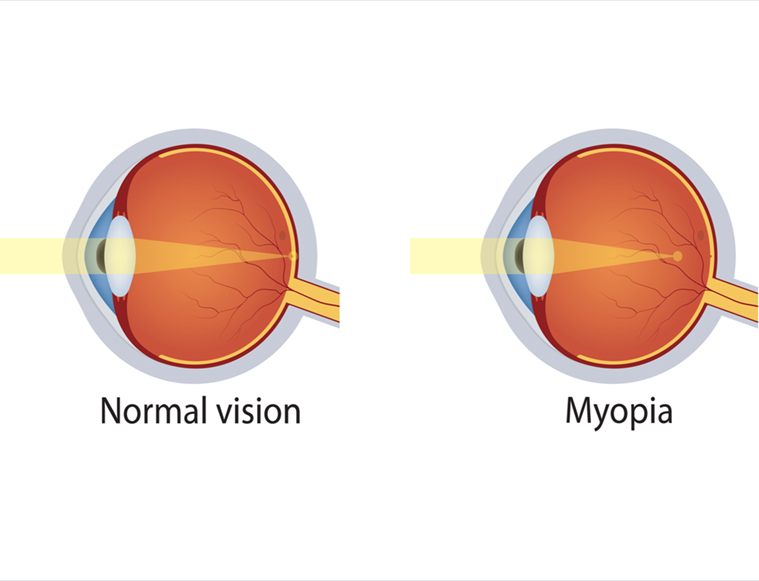
Myopia (Nearsightedness) refers to a condition where the distance vision is blurred. As a result the child has to wear minus powered glasses to see clearly. Myopia usually starts in School going children and increases rapidly in the age group of 5-15 years. High myopia is associated with risks of retinal problems, early onset cataract and glaucoma.
The condition occurs when the eyeball is too long or the cornea (the front part of the eye) has too much curvature, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it. Some common symptoms of myopia include:
1. Blurred distance vision.
2. Squinting.
3. Eyestrain.
4. Headaches.
5. Difficulty with night vision.
6. Holding objects close.
7. Difficulty in sports and outdoor activities.
8. Fatigue during close work.
History Taking & Questionnaire to assess risk factors:
Gathering relevant information about the patient's medical history and lifestyle factors through a questionnaire to understand potential risk factors associated with myopia development and progression.
Vision Assessment and Refraction:
The process of testing visual acuity and determining the appropriate lens prescription to correct myopia.
Basic Squint Evaluation:
A basic assessment of strabismus or squint to determine if there is any misalignment of the eyes, which may impact vision and require further evaluation.
Cycloplegic refraction after Dilatation & Retina Evaluation:
Cycloplegic refraction involves using eye drops to temporarily paralyze the eye's focusing mechanism, allowing for more accurate refractive measurements, while a retina evaluation checks for any abnormalities in the back of the eye.
Generation of Myopia Report:
A comprehensive report detailing the patient's myopia condition, test results, and treatment recommendations will be generated for reference and follow-up.
Treatment Recommendation by Doctor:
Based on the diagnosis and severity of myopia, the doctor will suggest suitable treatment options, which may include corrective lenses, atropine drops, orthokeratology, or other interventions.
Special Tests like Axial Length, Advanced Squint Evaluation, Orthoptics where needed:
In cases requiring specialized assessment, additional tests such as measuring the axial length of the eye, evaluating complex squints, or assessing eye coordination (orthoptics) may be performed.
Myopia Treatments are as follows:
Specialized spectacles (DIMS/HALT/Myocare): Customized glasses designed to slow down myopia progression in children.
Bifocal / Progressive glasses: Eyeglasses with different prescriptions in the upper and lower parts of the lenses to address near and distant vision.
Low-dose atropine drops: Eye drops containing a low concentration of atropine to help slow down the progression of myopia in children.
Orthokeratology: The use of specially designed gas-permeable contact lenses to reshape the cornea temporarily, providing clear vision without glasses or lenses during the day.
The aim of Myopia clinic at SRN is to identify children with myopia and treat them effectively so that they have clear vision and prevent the progression of myopia to high powers.
The most common symptom of myopia, or nearsightedness, is difficulty seeing distant objects clearly while having relatively clear vision for close-up tasks. Here are some common symptoms experienced by individuals with myopia:
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be indicative of other vision problems, so it's crucial to have a comprehensive eye examination performed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist to receive an accurate diagnosis. If you experience any of these symptoms or have concerns about your vision, it is recommended to seek professional eye care to determine the cause and appropriate management options.
Myopia, or nearsightedness, is diagnosed through a comprehensive eye examination performed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist. The diagnostic process typically involves the following steps :
By combining the results of these tests and examinations, the eye care professional can provide a definitive diagnosis of myopia and determine the appropriate treatment options, such as prescribing eyeglasses, contact lenses, or discussing refractive surgery if necessary.
Regular eye examinations are important to monitor the progression of myopia, especially in children, as early detection and intervention can help manage and control its development.