Diabetic Retinopathy: Early Signs and Effective Management
Diabetes is one of the deadliest diseases known to mankind. It affects about 1 in 11 people worldwide. As for…
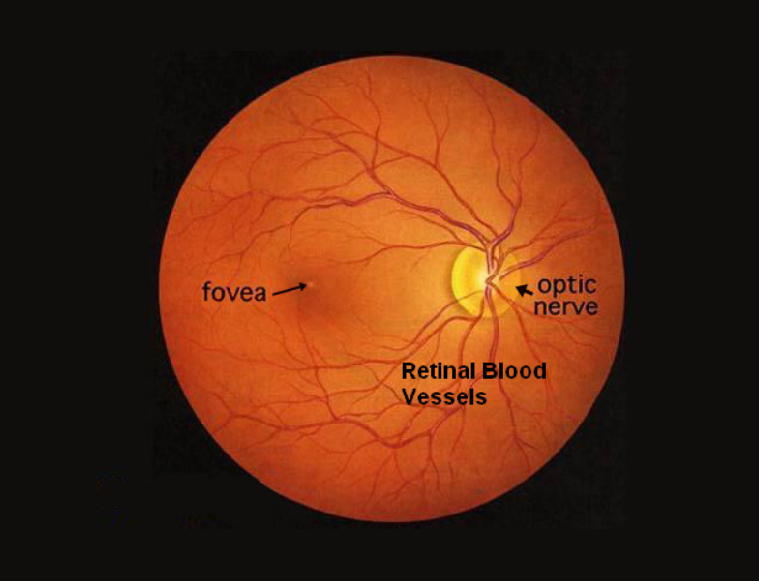
The retina is a layer of tissue located at the back of the eye. It contains specialized cells, including photoreceptors (rods and cones), that are responsible for capturing light and converting it into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to the brain through the optic nerve, where they are processed and interpreted as visual information. The retina plays a critical role in vision, allowing us to see and perceive the world.
Retinal diseases affect the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, leading to vision impairments or blindness. Common types include age-related macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment, and retinitis pigmentosa. Treatment options vary, including medication, laser therapy, and surgery. Early detection is vital to prevent vision loss.

OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
Non-invasive imaging for detailed retinal analysis, aiding in diagnosing conditions like macular degeneration and glaucoma.

Fundus Photo (Fundus Photography)
Quick and high-resolution images of the retina, helping detect abnormalities and monitor ocular health.

FFA (Fluorescein Angiography)
Evaluates blood flow in the retina and choroid, vital for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy and macular degeneration.

B-scan (B-Scan Ultrasonography)
Ultrasound-based imaging for visualizing eye structures when the view is obstructed, useful in detecting retinal detachments and tumors.

ERG (Electroretinogram)
Measures retina's electrical responses to light, crucial in diagnosing inherited retinal disorders and assessing overall retinal function.

OCT Angiography
OCT angiography is a non-invasive imaging technique that provides high-resolution, 3D visualisation of blood vessels in the retina and choroid.
Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of blindness in young and middle-aged adults, especially among those with diabetes. There are two types: Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR) and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR). NPDR is an early stage, often symptomless, but may lead to swelling and deposits in the retina. PDR poses a higher risk of vision loss, with abnormal blood vessel growth leading to complications like vitreous hemorrhage and retinal detachment.
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy vary from mild to severe visual disturbances, and regular eye exams are crucial for early detection. Dilated pupil exams and fluorescein angiography are commonly used for diagnosis.
Prevention involves strict blood sugar control, significantly reducing the risk of long-term vision loss. For those with diagnosed diabetic retinopathy, treatment options include corticosteroids and anti-VEGF drugs, while advanced cases may require vitreoretinal surgeries.
Shree Ramkrishna Netralaya offers specialized care for diabetic patients, providing routine screenings and medical management through treatments like laser therapy and anti-VEGF drugs. In advanced cases, skilled vitreoretinal surgeons perform vitrectomy procedures to address complications.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) is a progressive eye condition that primarily affects individuals over the age of 50, although it can occur earlier in some cases. The macula, a small area in the center of the retina responsible for sharp and detailed vision, degenerates over time, leading to a gradual loss of central vision. AMD can be classified into two types: Dry AMD, which is characterized by the accumulation of drusen (tiny yellow deposits) in the macula, and Wet AMD, wherein abnormal blood vessels grow beneath the retina and leak fluid, causing more rapid and severe vision decline.
While the exact cause of AMD remains unclear, age, genetics, smoking, and certain lifestyle factors are considered risk factors. Unfortunately, there is no cure for AMD, but early detection and treatment can help slow down its progression and preserve remaining vision.
Retinal vascular occlusion refers to the blockage of blood vessels supplying the retina, leading to impaired blood flow and potential damage to the retina.
LASER Treatment: Uses focused laser beams to seal abnormal blood vessels, reducing swelling and preventing further damage. Effective for certain types of retinal vascular occlusion like BRVO and CRVO.
LVA (Low Vision Aids): An optical/non-optical device that improves or enhances residual vision by magnifying the image of the object at the retinal level.
Imaging Techniques: Crucial for diagnosis and monitoring. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) provides cross-sectional retinal images, assessing damage and treatment effectiveness. Fluorescein angiography evaluates retinal blood flow with a fluorescent dye.
Intravitreal injections offer a targeted approach to treat various retinal conditions by delivering medications directly into the vitreous cavity at the back of the eye. Administered by trained Retina specialists, these injections effectively combat age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusion using anti-VEGF drugs. Additionally, intravitreal steroids aid in reducing inflammation associated with diabetic retinopathy, retinal vein occlusion, and uveitis. Infections, such as endophthalmitis and retinitis, can also be treated with antibiotics, antiviral, and antifungal drugs via intravitreal injections.
The eye and eyelids are anesthetized using drops or gel to ensure a painless experience, and sometimes a small numbing injection may be given, After cleaning the eye and eyelids with povidone-iodine, After cleaning the eye and eyelids with povidone-iodine, an eyelid speculum is used to keep the eyelids open during the procedure. The medication is then injected through the pars plana (the white part of the eye) using a small needle. Typically, patients feel minimal discomfort or pressure during the injection, which takes about 10 to 15 minutes to complete. Afterward, the speculum is removed, and the eye is cleaned.
Retinal detachment is a serious condition where the thin, light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye pulls away from its position, causing vision loss. Surgery aims to reattach the retina and prevent complications. Three types of surgery include:
Scleral Buckling: A silicone band or sponge supports the detached retina against the inner eye wall.
Vitrectomy: The surgeon removes the vitreous gel to access the retina, using a gas or oil bubble to push it back into place.
Pneumatic Retinopexy: A gas bubble is injected into the eye to push the detached retina, followed by laser or freezing treatment to seal it in place.
Posterior dislocation of the intraocular lens (IOL) or natural lens can occur after cataract surgery or severe ocular trauma, causing vision loss and discomfort. Surgery involves:
a) Pars Plana Vitrectomy: Removing the vitreous gel and dislocated lens material from the back of the eye. A new IOL may be inserted or left without one, depending on the patient's condition.
b) Anterior Chamber Lens Placement: In some cases, the dislocated lens is removed, and a new IOL is placed in the front part of the eye for visual correction.
Ocular trauma refers to eye injuries caused by accidents or sports incidents. Severity varies from mild abrasions to extensive damage to the retina and other eye structures. Severe cases may require surgery, including:
a) Repair of Retinal Tears or Detachment: Immediate surgical intervention is essential for retinal tears or detachment caused by trauma.
b) Repair of Ocular Structures: Damage to the cornea, iris, or lens may necessitate surgery to repair or replace these components for vision restoration.
There are several causes of retinal conditions and diseases. Some of the common causes include :
Signs and symptoms of retinal diseases and conditions can vary depending on the specific condition and its severity. However, there are some common signs and symptoms that may indicate a problem with the retina. These include :
It's important to remember that these signs and symptoms are general and can overlap with other eye conditions. If you notice any changes in your vision or experience any concerning symptoms, it's essential to seek an evaluation from an eye care professional. Early detection, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment can help preserve or improve your vision and prevent further complications.
The treatment for retinal diseases and conditions depends on the specific diagnosis, severity of the condition, and individual circumstances. Here are some common treatment approaches used for retinal diseases :
It's important to note that the specific treatment plan will be determined by an ophthalmologist or retina specialist based on the individual's condition and needs. Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are often necessary to assess the effectiveness of the treatment and make any necessary adjustments. Early detection, prompt treatment, and ongoing care can help maximize visual outcomes and preserve or improve vision in individuals with retinal diseases.
Risk factors for Retinal Diseases :
Diabetes is one of the deadliest diseases known to mankind. It affects about 1 in 11 people worldwide. As for…
Think about waking up on a random morning and finding a tiny red bump sitting on your eyelids. You touch…
Do you spend long hours staring at the screen or reading fine print? If so, you might have experienced tired…